By René Wadlow
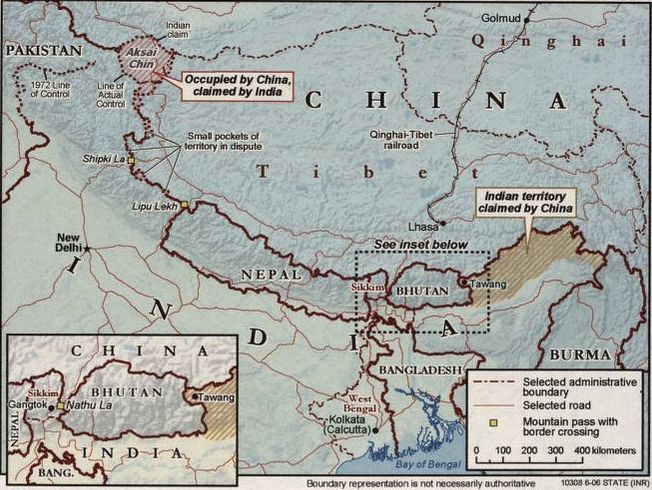
On April 22, 2025, four gunmen killed 26 people and injured others in the Kashmir tourist center of Pahalgam, Kashmir, India. The Resistance Front claimed responsibility for the Pahalgam attack, but the group is little known. Indian officials have blamed Pakistan as being behind the attackers saying that Pakistan has a fundamentally criminal disposition in its deep state membership. Pakistan is host to Islamic militants that carry out terrorist raids in India but does not necessarily control them.
As a result of the Pahalgam attack, India has closed its border crossings into Pakistan and suspended India’s 1960 Water Treaty with Pakistan. Anti-Pakistan protests have erupted in India’s capital New Delhi and in several other cities raising fears that anti-Muslim sentiment will grow in India. Pakistan responded by closing its border crossings with India and closed its air space to Indian aircraft.
In 2019, India modified the special self-governing status of Jammu and Kashmir, and security measures have been very tight since. Nevertheless, Kashmir is an important location for tourism within India. Within 48 hours, 90 percent of the tourists in Kashmir left – a blow to farmers who sold their food to tourists and to handicraft makers. The image of a young bride sitting beside her husband’s lifeless body has been viewed multiple times and is fixed into the Indian national consciousness as the symbol of the drama.
As tensions within Jammu and Kashmir have led to armed conflicts between India and Pakistan in the past, the governments of Russia, China, Saudi Arabia and Iran have offered their good offices as mediators. On April 25, Abbas Araghchi, the Iranian Foreign Minister, said that both India and Pakistan are “brother nations” and that Iran was prepared to play a mediation role.

It may be that the governments of Russia, China, Saudi Arabia, and Iran are all too involved with advancing their own political interests in world politics to be taken as neutral mediators. Nevertheless, the India-Pakistan tensions are very dangerous and may easily grow worse if steps to reduce tensions are not taken very soon.
As Citizens of the World, we are particularly called to help create a climate for negotiations in good faith and to reduce tensions. Therefore, we need to use our worldwide links in a creative way to reduce tensions. We devote ourselves to the safeguard, restoration, and construction of peace through dialogue, cooperation and reconciliation.
One approach in which World Citizens participate is called Track Two. Track One is official government-to-government diplomacy among instructed representatives of the State although there can be “back channels” and informal contacts among the representatives of governments. Track Two consists of discussions held among non-officials of conflicting parties in an effort to clarify outstanding disputes and to explore the options for resolving them in settings that are less sensitive and often less structured and with less media attention than those associated with official negotiations. Those involved in Track Two talks usually include scholars, senior journalists, former government officials and businesspeople. Depending on the aims and styles of these meetings, the profile of Track Two participants will differ.
The specific purposes of Track Two talks vary, but they are all related to reducing tensions. By informing their respective publics, participants, may indirectly contribute to the formation of new priorities and policies.
Track Two is not the end of the story for insights gained must be incorporated into the positions of government negotiators. There is a little verse by the Quaker economist Kenneth Boulding who participated in many Track Two efforts,
When Track One will not do,
We have to travel on Track Two.
But for results to be abiding,
The Tracks must meet upon some siding.
Today, discussions among Nongovernmental Organizations with avenues of communication to Indian and Pakistani officials should begin now. Time may be in short supply.
Prof. René Wadlow is President of the Association of World Citizens.